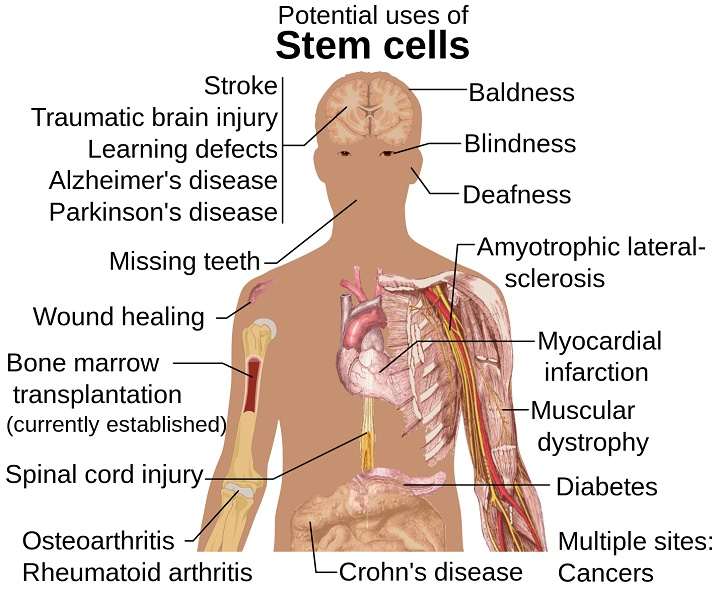
In recent years, the field of regenerative medicine has witnessed a remarkable advancement with the emergence of stem cell therapy. Stem cells, with their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, hold immense promise in treating a wide range of diseases and injuries. From neurological disorders to autoimmune conditions and degenerative diseases, the potential applications of stem cell therapy are vast and diverse. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the myriad of diseases that can be treated using stem cells, exploring the latest research findings and clinical applications.
Understanding Stem Cells: The Building Blocks of Regeneration
Before delving into the diseases treated by stem cells, it’s essential to understand the nature of stem cells themselves. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the remarkable ability to develop into specialized cell types. They can be broadly categorized into embryonic stem cells, derived from early-stage embryos, and adult stem cells, found in various tissues throughout the body. Additionally, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), generated from adult cells through reprogramming, offer another promising avenue for research and therapy.
Neurological Disorders: Harnessing Stem Cells for Brain Repair
Neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries, pose significant challenges due to the limited regenerative capacity of the nervous system. However, stem cell therapy offers hope for patients with these debilitating conditions. Research has shown promising results in using stem cells to replace damaged neurons, restore neural function, and promote tissue regeneration in the brain and spinal cord.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Stem cell-based approaches aim to replace lost neurons and enhance cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients.
- Parkinson’s Disease: Stem cell transplantation holds potential for replenishing dopamine-producing neurons and alleviating motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease.
- Spinal Cord Injuries: Stem cells have shown the ability to promote axonal regeneration and functional recovery in individuals with spinal cord injuries.
Cardiovascular Diseases: Repairing the Heart with Stem Cells
Cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, myocardial infarction, and peripheral artery disease, remain leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Stem cell therapy offers a promising strategy for repairing damaged cardiac tissue and restoring heart function. Various clinical trials have explored the use of stem cells, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and cardiac progenitor cells, to improve cardiac function and promote angiogenesis.
- Heart Failure: Stem cell transplantation aims to regenerate myocardial tissue and enhance cardiac function in patients with heart failure.
- Myocardial Infarction: Stem cells have shown potential for repairing infarcted myocardium and preventing adverse remodeling post-heart attack.
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Stem cell-based therapies seek to stimulate angiogenesis and improve blood flow to ischemic limbs in peripheral artery disease patients.
Autoimmune Disorders: Modulating the Immune Response with Stem Cells
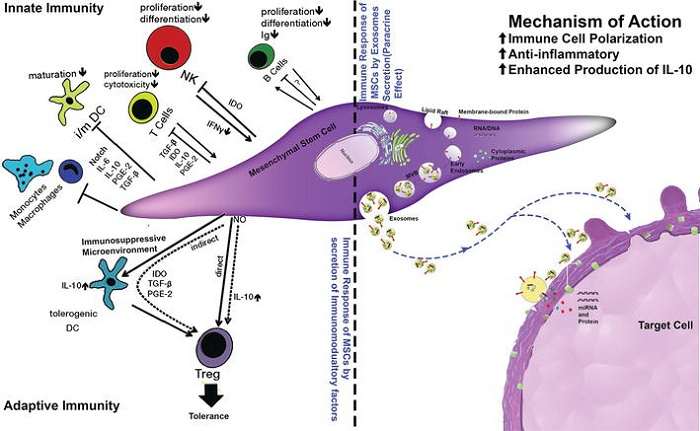
Autoimmune disorders arise from dysregulation of the immune system, leading to tissue damage and inflammation. Stem cell therapy offers a unique approach to modulate the immune response and induce tolerance towards self-antigens. Clinical studies have explored the use of stem cells, particularly hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), in treating autoimmune conditions such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Stem cell transplantation aims to reset the immune system and halt the progression of multiple sclerosis, reducing relapse rates and disability.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Stem cells have shown immunomodulatory effects, suppressing inflammation and preserving joint function in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Stem cell therapy offers a potential cure for systemic lupus erythematosus by restoring immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity.
Orthopedic Conditions: Repairing Musculoskeletal Tissues with Stem Cells
Orthopedic conditions, including osteoarthritis, tendon injuries, and bone fractures, present significant challenges due to limited regenerative capacity and poor healing outcomes. Stem cell-based approaches hold promise for promoting tissue repair and regeneration in musculoskeletal disorders. Clinical trials have investigated the use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), adipose-derived stem cells, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in treating orthopedic conditions.
- Osteoarthritis: Stem cell therapy aims to regenerate damaged cartilage and alleviate pain in osteoarthritis patients, potentially delaying the need for joint replacement surgery.
- Tendon Injuries: Stem cells have shown efficacy in promoting tendon repair and reducing scar tissue formation in patients with tendon injuries.
- Bone Fractures: Stem cell-based approaches seek to enhance bone healing and accelerate fracture repair by stimulating osteogenesis and angiogenesis at the injury site.
In conclusion, the list of diseases treated by stem cells continues to expand, offering new hope for patients grappling with debilitating conditions. From neurological disorders and cardiovascular diseases to autoimmune conditions and orthopedic injuries, stem cell therapy holds immense potential for tissue repair, regeneration, and immune modulation. As research progresses and clinical trials advance, the integration of stem cell-based approaches into mainstream medicine promises to revolutionize the treatment landscape, ushering in a new era of regenerative medicine and improved patient outcomes.