Opossums, with their unique appearance and nocturnal habits, often spark curiosity and, sometimes, fear. One common concern among people encountering opossums is whether these marsupials carry diseases that could pose a threat to human health. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the truth behind opossums and diseases, debunking myths while shedding light on potential health risks associated with these creatures.
Understanding Opossums: Nature and Behavior
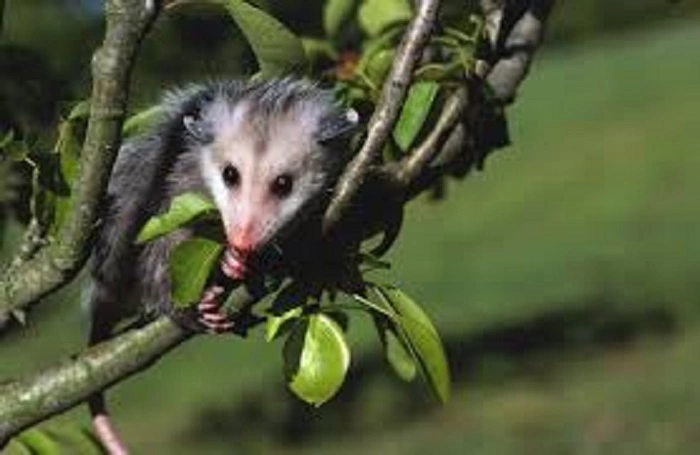

Before delving into disease transmission, it’s essential to understand the nature and behavior of opossums. Opossums are marsupials native to the Americas, known for their distinctive long, hairless tails, pointed snouts, and rat-like appearances. They are primarily nocturnal animals, meaning they are most active during the night.
Opossums are opportunistic omnivores, feeding on a varied diet that includes fruits, insects, small mammals, and carrion. They are also renowned for their unique defense mechanism of “playing dead” when threatened, a behavior known as “playing possum.”
Common Myths About Opossums and Disease Transmission
There are several misconceptions surrounding opossums and disease transmission. Debunking these myths is crucial for understanding the actual risks posed by these creatures:
Myth: Opossums Spread Rabies
- Fact: Contrary to popular belief, opossums have a lower body temperature than most mammals, making them less susceptible to the rabies virus. While it’s not impossible for opossums to contract rabies, documented cases are exceedingly rare.
Myth: Opossums Harbor a Plethora of Dangerous Diseases
- Fact: While opossums can carry certain diseases, the risk of transmission to humans is relatively low. Proper precautions, such as avoiding direct contact with wild opossums and practicing good hygiene, can further mitigate this risk.
Diseases Associated with Opossums
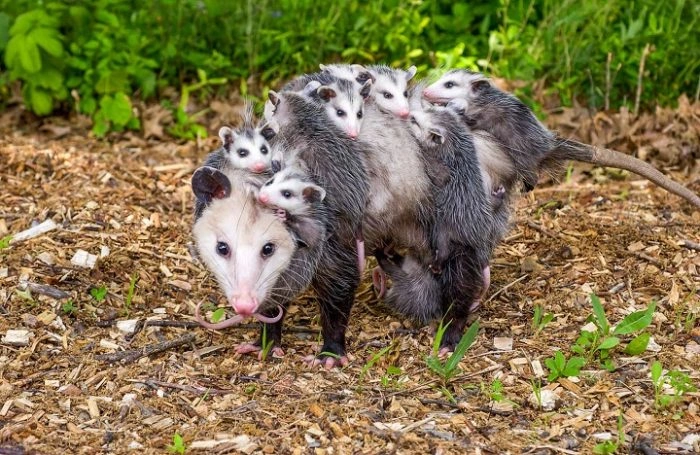

While the likelihood of contracting diseases from opossums is low, it’s still essential to be aware of potential health risks:
Leptospirosis
- Opossums can carry the bacteria responsible for leptospirosis in their urine. Humans may become infected through contact with contaminated water or soil. Symptoms of leptospirosis in humans include fever, headache, muscle aches, jaundice, and in severe cases, kidney damage.
Salmonellosis
- Opossums, like many wild animals, can carry Salmonella bacteria, which can cause food poisoning in humans. Salmonellosis symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, fever, and vomiting.
Tuberculosis
- While rare, opossums can contract tuberculosis (TB) and potentially transmit it to humans through respiratory droplets. However, cases of TB transmission from opossums to humans are extremely rare.
Ectoparasites
- Opossums may carry ectoparasites such as fleas, ticks, and mites, which can transmit diseases such as Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever to humans.
Preventive Measures and Tips for Coexistence
Despite the low risk of disease transmission from opossums, it’s essential to take precautions to minimize potential health risks:
Avoid Direct Contact
- Refrain from handling wild opossums or attempting to domesticate them. If you encounter an opossum in your vicinity, maintain a safe distance and allow it to move away on its own.
Secure Trash Bins
- Opossums are attracted to food sources such as garbage bins. Ensure that your trash bins are securely closed to deter opossums and other wildlife from scavenging.
Pet Care
- Keep pets indoors, especially at night, to minimize encounters with opossums and other wildlife. Additionally, regularly administer flea and tick prevention treatments to your pets.
Maintain a Clean Environment
- Remove potential food sources, such as fallen fruits or pet food, from your yard to discourage opossums from frequenting your property. Keep outdoor areas tidy to minimize hiding spots for wildlife.
Consult a Professional
- If you suspect an opossum infestation on your property or encounter a sick or injured opossum, contact local wildlife authorities or pest control professionals for assistance.
While opossums can carry certain diseases, the likelihood of disease transmission to humans is relatively low. By understanding opossum behavior, debunking myths, and implementing preventive measures, you can coexist with these fascinating creatures safely. Remember to respect wildlife and take necessary precautions to ensure the well-being of both humans and opossums in shared environment