Strep throat is a common bacterial infection caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria. It primarily affects the throat and tonsils, leading to symptoms like sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing. Many people wonder if a cough is a typical symptom of strep throat. This article explains whether strep throat causes coughing, what symptoms to expect, and when to seek medical attention.
What Is Strep Throat?
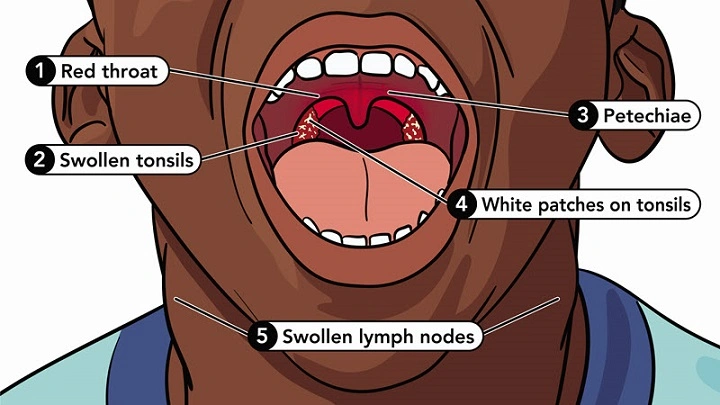
Overview of Strep Throat
Strep throat is an infection of the throat and tonsils caused by the Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria. It spreads easily through respiratory droplets and close contact.
Common Symptoms
- Sudden, severe sore throat
- Painful swallowing
- Red and swollen tonsils, sometimes with white patches or streaks of pus
- Fever and chills
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Headache and body aches
Does Strep Throat Cause a Cough?
Typical Symptom Profile
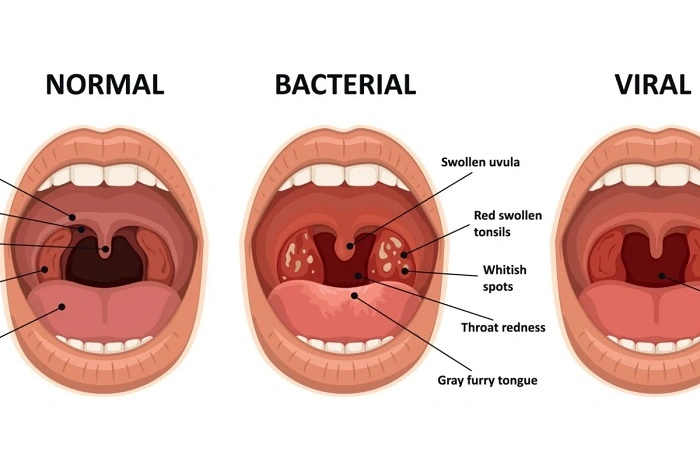
Unlike viral throat infections, strep throat usually does not cause a cough. A persistent cough is more often associated with viral infections like the common cold or flu.
Why Coughing Is Less Common
Strep throat primarily causes inflammation and infection in the throat and tonsils, not the lower respiratory tract where coughing reflexes are triggered.
When a Cough May Occur
Although uncommon, some people with strep throat might develop a mild cough due to throat irritation or concurrent viral infections.
Other Symptoms Sometimes Confused With Cough
Postnasal Drip
Nasal congestion and drainage can irritate the throat and trigger coughing, but this is usually related to allergies or viral infections.
Tonsil or Throat Irritation
Inflammation from strep can cause a tickling sensation in the throat, occasionally leading to a dry cough.
How to Differentiate Strep Throat From Other Causes of Cough
Presence of Fever and Severe Throat Pain
Strep throat often causes a high fever and severe sore throat without significant coughing.
Absence of Cold Symptoms
Runny nose, sneezing, and frequent coughing point more toward viral infections rather than strep.
Diagnostic Testing
A rapid strep test or throat culture performed by a healthcare provider can confirm the presence of strep bacteria.
When to See a Doctor
Symptoms Warranting Medical Attention
- Severe sore throat lasting more than 48 hours
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- High fever above 101°F (38.3°C)
- Swollen, tender lymph nodes
- Absence of typical cold symptoms but with throat pain
Importance of Diagnosis and Treatment
Prompt diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of strep throat can prevent complications such as rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation.
Treatment for Strep Throat
Antibiotics
A prescribed course of antibiotics effectively clears the bacterial infection and reduces symptom duration.
Supportive Care
- Rest and hydration
- Pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Throat lozenges and warm salt water gargles for soothing discomfort
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can strep throat cause a cough in children?
It’s rare, but some children may develop a mild cough if their throat is irritated or if they have a concurrent viral infection.
How long does strep throat usually last?
With antibiotics, symptoms typically improve within 2 to 3 days, but untreated strep throat can last longer and lead to complications.
Can you have strep throat without a sore throat?
Most people experience sore throat, but some may have mild or atypical symptoms. Testing is important for accurate diagnosis.
Is it contagious if I have strep throat but no cough?
Yes, strep throat spreads through saliva and respiratory droplets even without coughing.
How can I prevent spreading strep throat?
Practice good hygiene by washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact, and covering your mouth when coughing or sneezing.
Strep throat generally does not cause a cough, as coughing is more typical of viral respiratory infections. If you experience a severe sore throat without a cough, especially accompanied by fever and swollen lymph nodes, it may indicate strep throat. Proper diagnosis and timely treatment are essential to relieve symptoms and prevent complications. When in doubt, consult a healthcare professional for testing and care guidance.